|
|

|
|
|
|
|
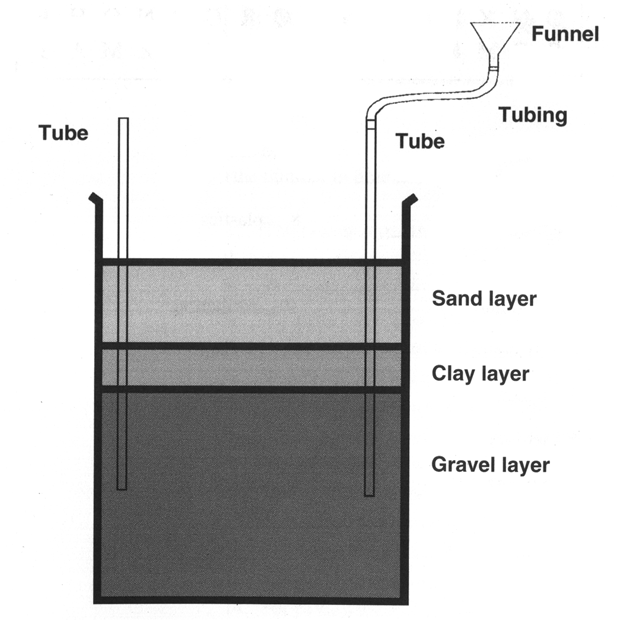
Objective:
To demonstrate how a fluid such as oil or water can flow out of
an underground reservoir and up to the surface.
To discover the characteristics of a reservoir (porosity/permeability)
and the important characteristics of a seal.
To investigate removal of fluids using a well.
Background Information:
The Theory and Principles
Materials:
Procedure:
Questions
|
Expected Answers
|
|
|